When it comes to payment card transactions, there are two key players involved: the card issuer and the card acquirer. Understanding the roles and differences between these entities is crucial for businesses seeking to navigate the complex world of payments.
In this article, we will delve deep into the nuances of the card acquirer and card issuer and clarify their roles and responsibilities.
The card acquirer, also known as the acquiring bank or merchant bank, plays a crucial role in facilitating credit and debit card transactions between merchants and cardholders' banks. Their primary responsibility is to ensure the smooth authorisation, settlement, and processing of these transactions.
The card issuer, also known as the issuing bank, plays a vital role in the payment card ecosystem by providing credit or debit cards to consumers. They are responsible for managing cardholder accounts, authorising transactions, and ensuring the availability of funds for cardholders.
The main differences between the two banks are the party they serve, and the role they play in a transaction. One bank operates on the cardholder’s side of the transaction, and the other mainly focuses on merchants who serve them.
Here’s a quick breakdown of some of the key differences the define the issuer vs acquirer dynamic:
|
|
Acquirer |
Issuer |
|
Customer base |
Acquirers primarily focus on establishing and maintaining relationships with merchants, providing them with the necessary tools and support to accept card payments.
|
Issuers concentrate on building relationships with cardholders, offering credit facilities, loyalty programs, and security measures.
|
|
Financial liability |
Acquirers assume financial liability for fraudulent transactions, chargebacks, and operational risks associated with payment processing.
|
Issuers bear the ultimate financial liability for unauthorised transactions, fraud, and credit risk.
|
|
Revenue sources |
Acquirers generate revenue through merchant discount fees, transaction processing fees, and value-added services.
|
Issuers earn revenue through cardholder interest charges, annual fees, interchange fees, and other cardholder-related charges.
|
|
Customer base |
Acquiring banks cater to merchants, offering services that enable these businesses to accept and process (or “acquire”) card payments.
|
Issuing banks serve cardholders, providing them with (or “issuing”) credit and debit cards. |
|
Risk and responsibility |
Acquiring banks manage risks related to merchant transactions; for instance, fraud and chargeback liability. |
Issuing banks bear the credit risk associated with their cardholders. They must ensure that the cardholders are capable of repaying their debts. |
|
Interaction with payment networks
|
Acquiring banks are more involved in the technical and operational aspects of payment processing, including ensuring secure and efficient transaction processing for merchants.
|
Issuing banks interact more directly with cardholders in terms of managing accounts, addressing customer service issues, and ensuring compliance with credit regulations. |
These differences underline the distinct, yet complementary roles that an issuer vs acquirer plays in the payments ecosystem. These positions are vital to ensure that payment transactions can be conducted efficiently.
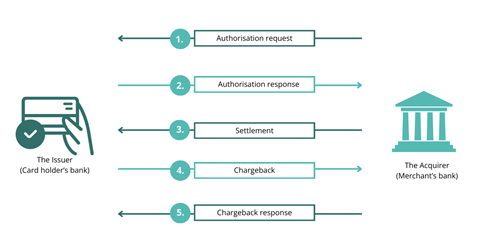
When it comes to transactions and chargebacks, issuers and acquirers play different, but important roles. Let's break down the steps involved in this process:
It's important to note that chargebacks can have financial implications for merchants. Acquirers may impose fees on merchants with high chargeback rates, and in some cases, terminate their accounts if chargeback rates become too high.
In summary, issuers and acquirers work together to facilitate transactions and manage chargebacks. The acquiring bank handles the payment process on behalf of the merchant, while the issuing bank represents the customer and decides the outcome of chargeback disputes.
In summary, the card acquirer and card issuer play integral roles in the world of payments. The card acquirer is responsible for processing transactions for merchants and ensuring that the funds are transferred to their accounts. On the other hand, the card issuer acts as the representative of the customer, verifying the card's validity and checking the customer's credit or funds availability.
Understanding the nuances and distinctions between card acquirers and card issuers is paramount for businesses aiming to thrive in the dynamic payments landscape. By grasping the unique roles, responsibilities, and competitive advantages of these entities, businesses can make well-informed decisions, cultivate stronger partnerships, and unlock their maximum revenue potential.
Say goodbye to complex payment systems and hello to simplicity. Get in touch today to find out more about our payments solutions.

Covering various aspects of selecting a PSP, this blog explores the importance of flexible solutions, customer focus, competitive pricing, and being backed by experienced professionals.
Read now
In this blog, we will delve into the realm of online payments and explore the intricacies of setting up a merchant account. In today's digital age, having a merchant account is imperative for businesses seeking to embrace online payment solutions.
Read now